Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common adult joint disease and predominantly involves the weight-bearing joints.1 This condition, including spondylosis (OA of the spine), results in significant disability and resource utilization and is a leading cause of medical separation from military service.2 A recent MSMR analysis described the incidence of OA and spondylosis diagnoses among active component service members of the U.S. Armed Forces from 2016 through 2020.3 During the 5-year surveillance period, crude overall rates of incident OA and spondylosis diagnoses were 630.9 per 100,000 person-years (p-yrs) and 958.2 per 100,000 p-yrs, respectively.3 Anatomic site-specific rates of OA varied by sex, race/ethnicity group, service, and military occupation.3
In this analysis, the numbers and percentages of incident cases of OA and/or spondylosis with a medical separation after the incident diagnosis (through 31 July 2021) were stratified by selected demographic and military characteristics. Separations from service were categorized as having been for medical reasons using interservice separation (ISC) codes (1010, 1011, 1012, 1013, 1014, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013).
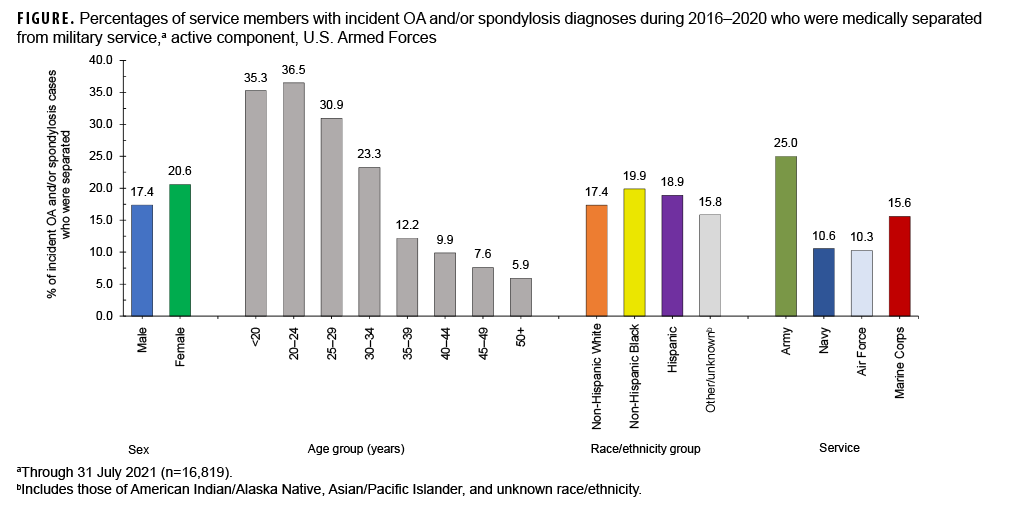
Among a total of 94,036 unique individuals who qualified as incident cases of OA and/or spondylosis during 2016–2020, 17.9% (n=16,819) were medically separated from service by July 31, 2021 (data not shown). The median time from incident OA and/or spondylosis diagnosis and separation from military service was 430 days (mean=506 days) (data not shown). Median times to separation were broadly similar by demographic characteristics (sex, age group, and race/ethnicity group) with more pronounced differences apparent by service; the median time to separation was lowest for Army and Marine Corps members (392 days and 447 days, respectively) and highest for Air Force members (553 days) (data not shown). The percentages of incident cases aged 34 years or younger (range=23.3%–36.5%) who were medically separated were higher than the percentages among those aged 35 or older (range=5.9%–12.2%) (Figure). Army members with incident diagnoses of OA and/or spondylosis were more likely to be medically separated compared to their respective counterparts in the other services.
References
1. Abramoff B, Caldera FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293–311.
2. Patzkowski JC, Rivera JC, Ficke JR, Wenke JC. The changing face of disability in the US Army: the Operation Enduring Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom effect. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20 (Suppl 1):S23.
3. Williams VF, Ying S, Stahlman S. Update: Osteoarthritis and spondylosis, active component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2016–2020. MSMR. 2021;28(12):2–13.